Animal poisons and venoms are sources of biomolecules naturally chosen. Rhinella schneideri toads are widespread in the entire Brazilian territory they usually have poison glands and mucous gland. Lately, protein from toads’ secretion has gaining consideration. Frog pores and skin is broadly identified to current nice variety of host protection peptides and we hypothesize toads current them as effectively.

On this research, we used a RNA-seq evaluation from R. schneideri pores and skin and biochemical exams with the gland secretion to unravel its protein molecules. We recognized novel toxins and proteins from R. schneideri mucous glands. Apart from, this can be a pioneer research that introduced the in depth characterization of protein molecules richness from this toad secretion. The outcomes obtained herein confirmed proof of novel AMP and enzymes that should be additional explored.
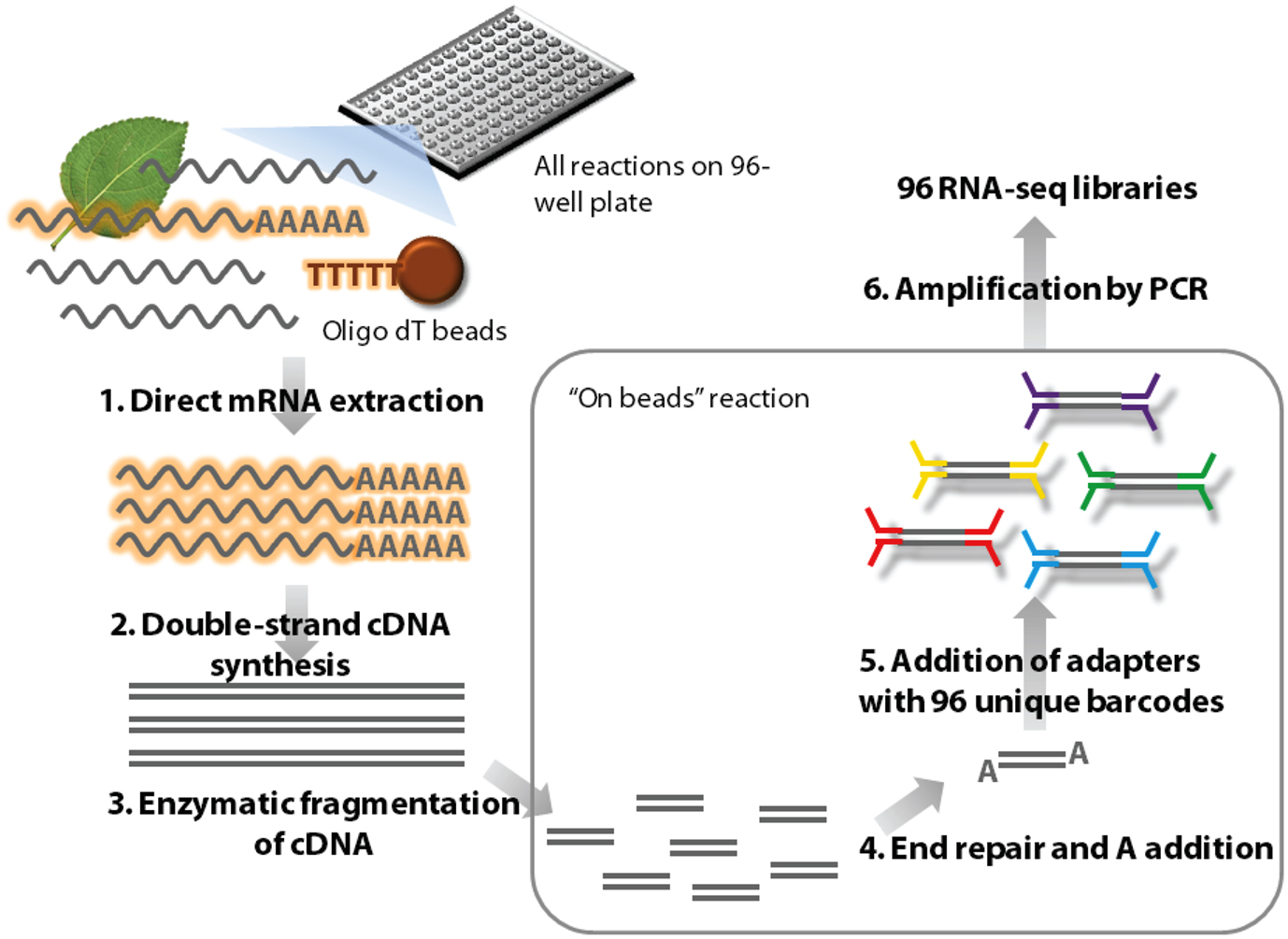
Whole RNA from the toad pores and skin was extracted utilizing TRizol reagent, sequenced in duplicate utilizing Illumina Hiseq2500 in paired finish evaluation. The uncooked reads have been trimmed and de novo assembled utilizing Trinity. The ensuing sequences have been submitted to purposeful annotation in opposition to non-redundant NCBI database and Database of Anuran Protection Peptide.
Moreover, we carried out caseinolytic exercise check to evaluate the presence of serine and metalloproteases in pores and skin secretion and it was fractionated by quick liquid protein chromatography utilizing a reverse-phase column. The fractions have been partially sequenced by Edman’s degradation.

We have been in a position to determine a number of lessons of antimicrobial peptides, resembling buforins, peroniins and brevinins, in addition to PLA2, lectins and galectins, combining protein sequencing and RNA-seq evaluation for the primary time. As well as, we might isolate a PLA2 from the pores and skin secretion and infer the presence of serine proteases in cutaneous secretion.
The extracted RNA was freed from PCR inhibitors and may very well be synthesized into complementary DNA and used for profitable relative quantification of ocular floor biomarkers by quantitative real-time PCR. For gene targets current in low abundance, complementary DNA may be used for quantification by the comparatively new and rising technique of droplet digital PCR.
The described technique was efficiently used to guage three biomarkers in a scientific trial assessing the tolerability of a proprietary eyelid remedy in 92 IC samples from a research inhabitants of 46 individuals
Comparative analysis of 5 protocols for protein extraction from stony corals (Scleractinia) for proteomics.
Corals particularly the reef-building species are crucial to marine ecosystems. Proteomics has been used for researches on coral ailments, bleaching and responses to the setting change. A strong and versatile protein extraction protocol is required for coral proteomics. Nonetheless, a comparative analysis of various protein extraction protocols remains to be not obtainable for proteomic evaluation of stony corals.
Within the current research, 5 protocols have been in contrast for protein extraction from stony corals. The 5 protocols have been TRIzol, phenol-based extraction (PBE), trichloroacetic acid (TCA)-acetone, glass bead-assisted extraction (GBAE) and a commercially obtainable equipment. PBE, TRIzol and the business equipment have been extra sturdy for extracting proteins from stony corals.
The protein extraction effectivity and repeatability, two dimensional electrophoresis (2-DE) and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI TOF MS) have been employed to guage the protocols. The outcomes indicated that PBE protocol had the higher protein extraction effectivity than the others.
Protein extraction protection diversified among the many procedures. Every protocol favored for sure proteins. Due to this fact, it is extremely necessary for coral proteomic evaluation to pick out an appropriate protein protocol upon the experimental design. Generally, PBE protocol may be the primary selection for extracting proteins from stony corals.